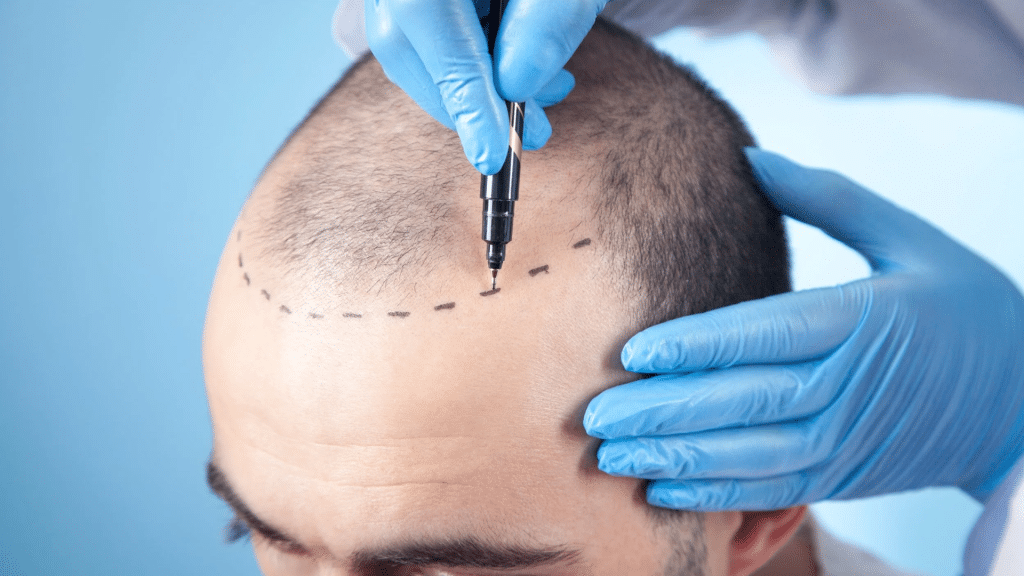
Have you ever looked in the mirror and wondered if a hair transplant could really help your receding hairline?
I’ve been there, searching for clear, honest information about what the procedure actually involves and what I could realistically expect.
I know it can feel overwhelming; there’s so much conflicting advice online, but I’ve spent time digging into the details, talking to professionals, and learning from real experiences.
In this blog, I want to share what I’ve learned about hair transplant procedures, from how they’re done to what kind of results you can expect.
I’ll be upfront about success rates and the things you need to consider before taking the step.
My goal is simple: to give you the information you need to make a confident, informed choice about restoring your hair and feeling like yourself again.
What Is a Hair Transplant?
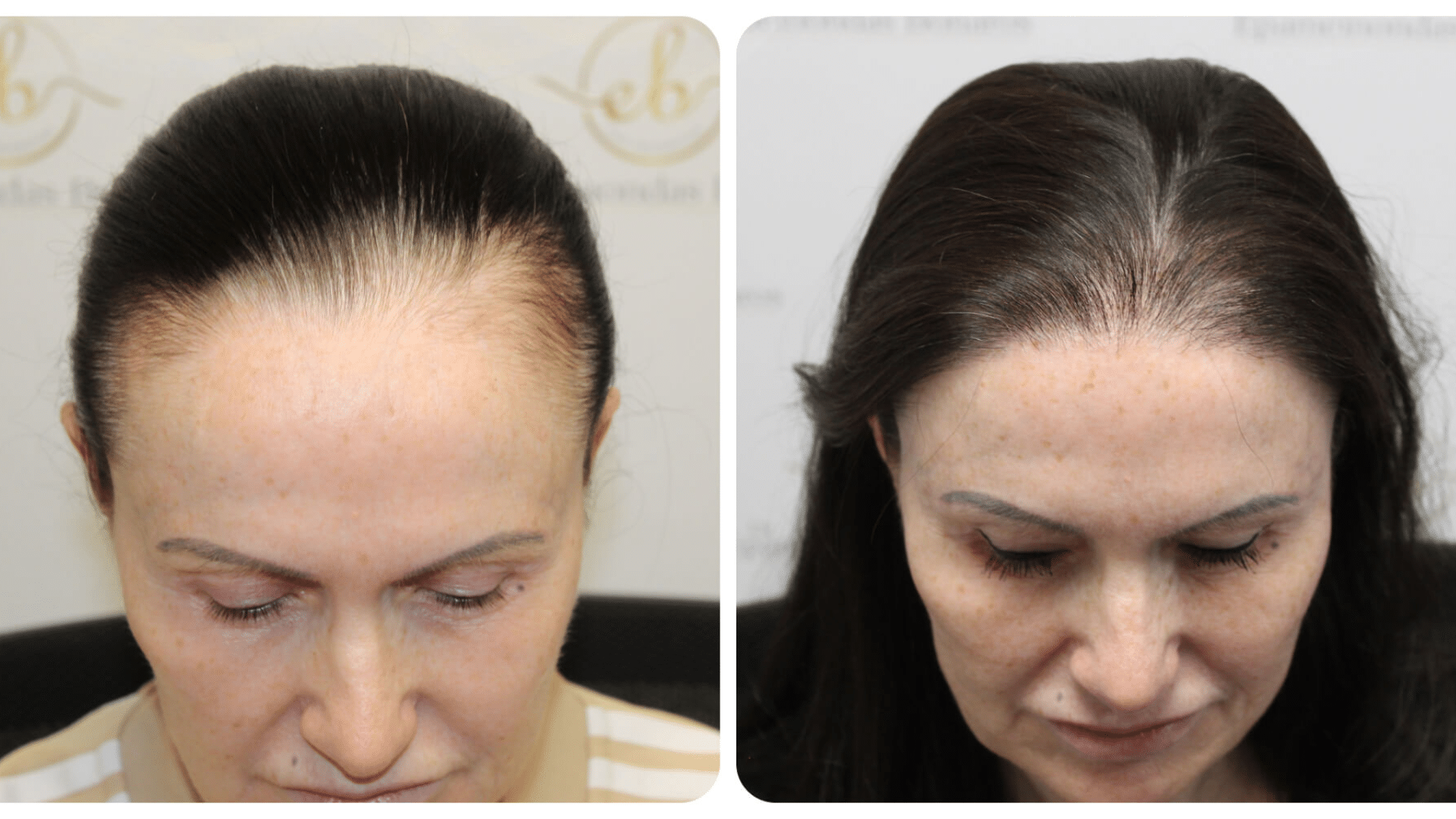
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that moves hair follicles from one part of the scalp, called the donor site, to areas with thinning or baldness, known as the recipient site.
This technique encourages natural hair growth in the treated area and offers a long-lasting solution.
Usually, the transplanted follicles come from areas resistant to hair loss, like the back or sides of the head.
Hair transplants differ from other hair restoration methods, which focus on stimulating existing hair through non-surgical treatments such as medication, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, or low-level laser therapy.
Unlike these approaches, hair transplants provide permanent, natural-looking results by relocating actual follicles.
Hairline restoration is a targeted form of hair transplant designed to rebuild or improve the front hairline. It focuses on shaping and densifying the hairline to create a fuller, youthful frame.
In short, hair transplants are a permanent surgical solution, and hairline restoration is a precise application for improving receding hairlines.
Hairline Surgery: An Alternative to Hair Transplants
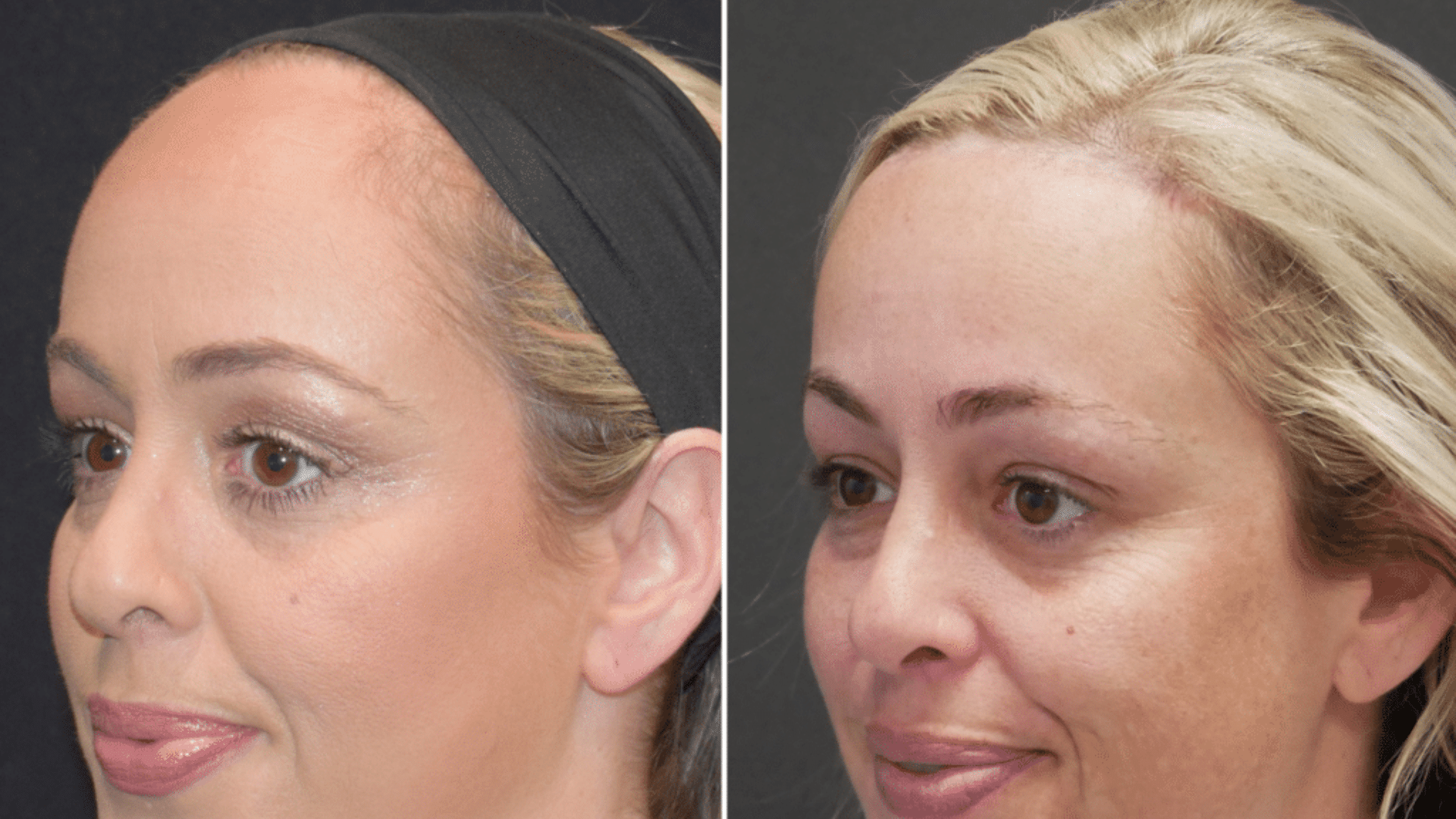

Hairline surgery, also known as hairline lowering or forehead reduction, is a cosmetic procedure designed to bring the hairline closer to the eyebrows, reducing forehead height and creating a balanced facial appearance.
The process starts with a consultation where the surgeon assesses facial structure and designs a natural-looking hairline.
The procedure typically takes 2 to 4 hours under local anesthesia or sedation. The surgeon makes an incision along the existing hairline, often in a zig-zag or irregular trichophytic pattern to minimize visible scarring.
A section of forehead skin is removed, and the scalp is pulled forward and secured, effectively lowering the hairline. The incision is sutured to blend with natural hair growth, and excess skin is trimmed for a smooth transition.
Post-surgery, patients may experience swelling and tightness in the forehead and must follow aftercare instructions carefully. Recovery involves managing swelling and avoiding strenuous activity for several weeks.
Unlike hair transplants, this procedure repositions the hairline, offering immediate, permanent results and a boost in facial aesthetics and confidence.
Types of Hair Transplant Procedures
Hair transplants are mainly performed using two methods, FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) and FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction), each designed to move healthy hair follicles to thinning or receding areas. Let’s discuss both:
1. FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation)
In FUT, a strip of scalp tissue is surgically removed from the donor area, usually at the back of the head.
This strip is dissected under a microscope into individual follicular units, which are then transplanted into the thinning or bald areas.
The surgeon carefully creates recipient sites to match natural hair direction and density. FUT is effective for extensive hair loss or full hairline restoration.
Pros:
- Can yield a large number of grafts in a single session
- Generally, more cost-effective than FUE
- Produces very high graft survival rates.
Cons:
- Leaves a linear scar at the donor site
- Longer healing time
- More postoperative discomfort
2. FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction)
FUE involves extracting individual hair follicles from the donor area using a small punch tool, selecting the healthiest ones for transplantation.
Each follicle is implanted into the recipient area with care, following the natural direction and angle of existing hair to ensure proper growth and density.
FUE avoids a linear scar and has a shorter recovery period, making it ideal for short hairstyles and minimal visible scarring.
Pros:
- No linear scar
- Shorter recovery period
- Less invasive with minimal discomfort
Cons:
- More time-consuming than FUT
- It can be more expensive
- Requires high precision to avoid follicle damage
Step-by-Step Hair Transplant Procedure
Let’s see an overview of a typical hair transplant, focusing on FUE but applicable to most hair restoration procedures:
- Initial Consultation and Diagnosis: The surgeon assesses your hair loss, discusses goals, and plans the hairline and recipient areas.
- Preparing the Scalp: The donor area (usually back and sides) is cleaned and sometimes shaved for precise follicle extraction.
- Local Anesthesia: A Local anesthetic is applied to numb both the donor and the recipient areas for a comfortable procedure.
- Extraction of Hair Follicles: Individual follicles are removed with a tiny punch tool and stored in a solution to maintain viability.
- Graft Preparation and Sorting: Follicles are trimmed, sorted, and kept sterile for implantation.
- Recipient Site Creation: Small incisions are made in the thinning or receding areas at specific angles to mimic natural hair growth.
- Implantation of Grafts: Follicles are implanted carefully to ensure correct direction, density, and a natural-looking hairline.
- Aftercare and Healing: The scalp may be bandaged, and instructions include avoiding touching grafts, keeping them hydrated, and taking medications. Follow-ups monitor growth.
The procedure can take several hours and may require multiple sessions for extensive restoration. Transplanted follicles retain natural resistance to hair loss, providing long-lasting, natural results.
Hair Transplant Recovery and What to Expect
Recovery after a hair transplant is gradual, with visible results appearing over several months. Understanding the timeline, potential side effects, and proper aftercare helps set realistic expectations and ensures optimal outcomes.
Timeline for Results
Hair transplant results appear gradually over several months. Each stage, from initial healing to full hair growth, reflects natural hair restoration.
- 0–14 Days – Initial Healing: The scalp begins to recover, small scabs form around transplanted follicles, and minor discomfort or swelling is common.
- 1–2 Months – Shedding Phase: Transplanted hairs often fall out, which is normal. The scalp may temporarily look similar to before the procedure.
- 3–5 Months – Early Growth: New hairs start growing slowly, usually thin and fine, gradually filling in the transplanted areas.
- 6–8 Months – Mid-Stage Growth: Hair density improves, and the hairline starts taking its final shape.
- 9–12+ Months – Final Results: Hair reaches full thickness, blends naturally with existing hair, and offers a permanent, long-lasting look.
Possible Side Effects
Mild swelling, redness, and scabbing are common after a transplant. Rare complications may include infection, folliculitis, or temporary shedding of nearby hairs.
- Swelling and Redness: Mild inflammation around donor and recipient sites is typical.
- Scabbing and Itching: Normal during healing; should not be picked or scratched.
- Shock Loss: Nearby natural hairs may temporarily shed.
- Infection or Folliculitis: Rare, usually preventable with proper aftercare.
- Scarring: FUT may leave a linear scar; FUE typically leaves tiny, less noticeable dot scars.
Tips for Better Outcomes
Following post-op care, avoiding strain, and using prescribed treatments help ensure optimal results. Patience and regular follow-ups are key to healthy, lasting growth.
- Follow Aftercare Instructions: Keep the scalp clean, moisturized, and avoid touching the grafts.
- Limit Physical Activity: Avoid heavy workouts, sweating, or sun exposure for the first couple of weeks.
- Medication Compliance: Use prescribed medications or topical treatments exactly as advised.
- Be Patient with Growth: Visible improvement takes several months; early hair may look thin, but it will thicken over time.
- Consider Adjunct Treatments: Minoxidil or PRP therapy may support growth after the shedding phase.
- Attend Follow-Ups: Regular check-ins with your surgeon help track progress and address any concerns.
Hair Transplant Success Rates and Patient Outcomes
The success rate of hair transplant procedures is generally very high, with most studies and expert sources reporting graft survival rates between 85% and 98%, depending on the technique and individual factors.
- FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): Success rates range from 90% to 98%.
- FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): Typically ranges from 80% to 95%.
On average, modern hair transplants achieve 90–95% graft survival, meaning roughly 9 to 10 out of every 10 transplanted follicles successfully grow in the recipient area within 12–18 months.
Key factors affecting success include the surgeon’s skill, the chosen technique, patient hair characteristics, and adherence to post-operative care. At reputable clinics, failure rates are very low, often below 2%.
Patient satisfaction is also high, with surveys reporting average ratings around 8.3 out of 10 several years after treatment, and some clinics noting success rates as high as 97–100%.
When performed correctly, hair transplants provide a permanent, natural-looking result with long-lasting, robust hair growth.
Hair Transplant Costs: What to Expect
Hair transplant costs can vary widely based on factors like the number of grafts, the technique used (FUE or FUT), the surgeon’s expertise, and the clinic’s location.
A typical full procedure generally ranges from $4,000 to $15,000 or more.
- Costs are often calculated per graft, typically $3 to $10 each. Smaller procedures, such as hairline restoration, require fewer grafts, lowering the overall cost.
- Moderate hair loss needing 1,000–2,000 grafts may cost $4,000–$12,000.
- Extensive bald areas requiring 3,000–6,000 grafts can range from $10,000–$15,000+.
Additional expenses may include consultation fees, pre-surgery tests, anesthesia, medications, and follow-up visits.
Choosing an experienced surgeon is key to achieving natural, long-lasting results, even if it means higher costs. Many clinics also offer payment plans or financing options to make the procedure more affordable.
Conclusion
I hope this guide has given you a clear understanding of hair transplants, from recovery timelines and side effects to success rates, costs, and the differences between FUT and FUE.
I know how overwhelming hair loss can feel, and how important it is to find a solution that works and looks natural.
I want you to feel confident that the information here addresses your concerns about effectiveness, safety, and long-term results.
By following professional advice and proper aftercare, you can maximize your chances of a successful transplant and enjoy lasting, natural-looking hair.
I’ve shared insights on what to expect, the factors influencing success, and tips for choosing the right procedure, so you can move forward with knowledge, patience, and peace of mind.